Google Ads API campaign type
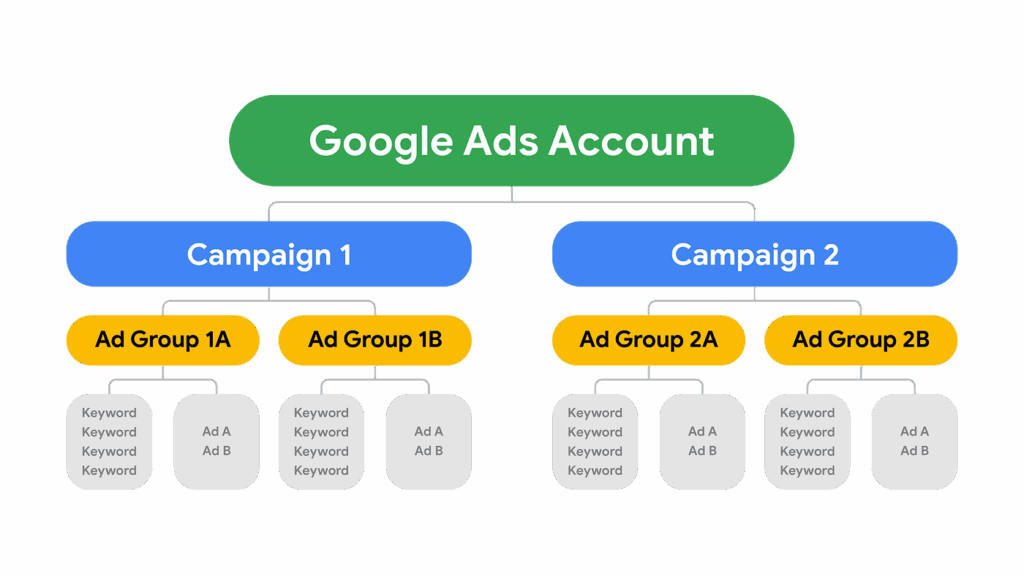
The Google Ads API campaign type becomes a crucial foundation for controlling performance and keeping data transparent. Each Google Ads API campaign type operates according to its own logic, directly influenced by input signals, budget level, and how the platform handles distribution. When deploying in an enterprise environment, the campaign structure not only determines the machine learning speed but also governs the long-term scalability. Therefore, understanding how signal groups interact, the flexibility of each campaign type, and the data threshold that each API needs will help you be more proactive in designing, monitoring, and refining your advertising operations.
Shaping the Structure of Google Ads API Campaign Types
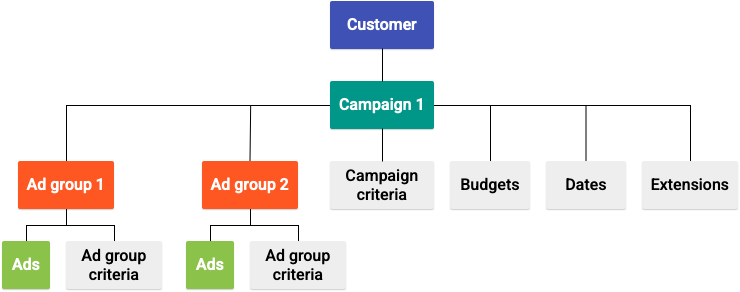
Each Google Ads API campaign type comes with its own objectives, its own way of collecting signals, and a distinct level of automation. This makes the selection process clearer, especially when you need to scale efficiently or maintain tight performance control in complex environments. To understand the full picture, we need to break down each campaign group and how the API processes the internal distribution flow.
Search Campaigns
Search campaigns operate based on real query signals. The API focuses on interpreting intent, evaluating goals, and adjusting bids per session. Query data is continuously aggregated to understand user habits over time. This mechanism allows ads to meet real demand, particularly when a brand is targeting users with clear intent and high readiness to act.
Shopping Campaigns
Shopping campaigns prioritize product attribute data. The API processes elements such as price, images, descriptions, and relevance to determine the right serving moment. When product data is clean and updated consistently, distribution becomes smoother and more predictable. For e-commerce brands, this is a core foundation for improving conversion rates.
App Campaigns
App campaigns aim to drive installs or deeper in-app engagement. The API analyzes real-time behavior to identify the users most likely to act. This helps allocate budget effectively and keeps the machine learning process fast. When installs reach a stable pace, the campaign naturally scales without causing budget volatility.
Display Campaigns
Display campaigns expand visibility across websites and apps. The API evaluates browsing behavior, content context, interests, and placement quality to choose appropriate environments. In this campaign group, contextual signals carry significant weight, helping the system place ads where users are most receptive.
Video Campaigns
Video campaigns leverage YouTube’s extensive content ecosystem. The API monitors actions such as watch time, interactions, and skip behavior to determine distribution. These signals allow the system to assess content appeal and adjust reach in real time.
Performance Max Campaigns
This format represents the highest level of automation. The API connects signals from Search, Display, YouTube, and Shopping to find users with the highest conversion potential. This campaign type suits businesses seeking broad performance gains without manually segmenting multiple campaigns.
Discovery Campaigns
Discovery and Demand Gen campaigns reach users before a clear need has formed. The API analyzes browsing patterns to detect audiences likely to develop interest. When implemented properly, this campaign type expands the brand’s reach and builds new customer pipelines naturally.
Hotel Campaigns
Hotel campaigns support the travel sector, where data shifts rapidly with seasonality and user behavior. The API tracks room availability, pricing, and search trends to optimize each impression. This ensures travel brands reach potential customers at the right moment and increase booking likelihood.
Organizing API Data for Precise Operation

When building an integrated API system for advertising, the most important factor is maintaining clean, structured data. Platforms like Google Ads operate entirely on signals, and each signal only works effectively when delivered correctly. A clear data structure helps the API understand context, classify requests properly, and return consistent results. With well-organized data, measurement, synchronization, and analysis become significantly easier.
Defining Core Data Fields
An API system only becomes strong when all data fields are clearly defined. Core fields such as campaign objectives, behavioral signal types, distribution configurations, and measurement indicators must be named clearly, without overlap or ambiguity. When the API receives consistent fields, the platform can understand context accurately and process requests without signal errors. This is especially crucial in automated campaigns, where even small inconsistencies can push distribution toward irrelevant audiences.
In reality, many accounts run into data issues simply because fields are inconsistent across campaigns or across touchpoints. Standardizing early helps reduce risk, increase processing speed, and minimize debugging time. Clean data also accelerates machine learning since the algorithm receives high-quality signals throughout the journey.
Structuring Audiences and Events
Next, you need a well-organized structure for audiences and events to avoid signal noise. Each event such as view content, add to cart, or submit form should be separated clearly and assigned the correct value. When the API recognizes distinct event hierarchies, it can evaluate user behavior more accurately and map conversion paths clearly.
Structured event data also helps you trace sources quickly during deeper analysis. With clean signals, reporting becomes easier to read and track. Many brands overlook this step, yet it directly affects conversion measurement. When every event is properly identified, the system strengthens its signaling and distributes more confidently to the right audiences.
Synchronizing Data Across Platforms
An API cannot operate accurately if data drops or becomes inconsistent at any point. When connecting multiple platforms such as CRM, website, ad systems, and internal data processors, you must ensure data is uniform everywhere. Misaligned data not only confuses the algorithm but also produces unreliable reports.
Synchronization keeps the entire signal flow smooth. A system receiving consistent data returns stable results, reduces distribution errors, and limits fluctuations in conversion metrics. This is a key advantage for automated campaign types, especially those relying heavily on machine learning.
Synchronization also involves version control, format validation, source tagging, and ensuring updates propagate correctly across platforms. With a seamless data flow, you can scale campaigns confidently without worrying about signal distortion.
Verifying Data Reliability and Adjusting Issues
Finally, an API system stays accurate only when you routinely verify every data source. Metrics such as event capture rate, signal frequency, event structure stability, and duplicate values must be monitored consistently. If discrepancies emerge, adjustments are required immediately to avoid long-term damage to the algorithm.
A reliable data structure keeps analysis clear and reduces risk as you scale. This ensures long-term stability and supports decision-making based on trustworthy data.
Contact Info
We provide services google account for rent nationwide, and with a team of experienced and qualified staff who both support advertising and can directly perform Facebook advertising if you need. Contact us via phone number.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can rely on three core signals. First, the event logging rate becomes stable and no longer fluctuates irregularly by the hour. Second, delivery or conversion metrics start showing reduced noise, without sudden unreasonable spikes. Third, the system stops generating false alerts related to event definitions. When all three signs appear together, it means the API has completed its adaptation phase and is now responding accurately to the updated data structure.
Even clean data can be misunderstood when the context does not align. The API relies on machine learning models, which are highly sensitive to changes in frequency, priority, or signal ordering. To detect the issue, you should monitor the gap between raw data and what appears in the reports. If the system records significantly fewer or more events than reality, the API is likely misdefining the context. In that case, review your event dispatch rules, naming conventions, and placement of tracking code to eliminate discrepancies.