Negative keywords Shopping campaigns
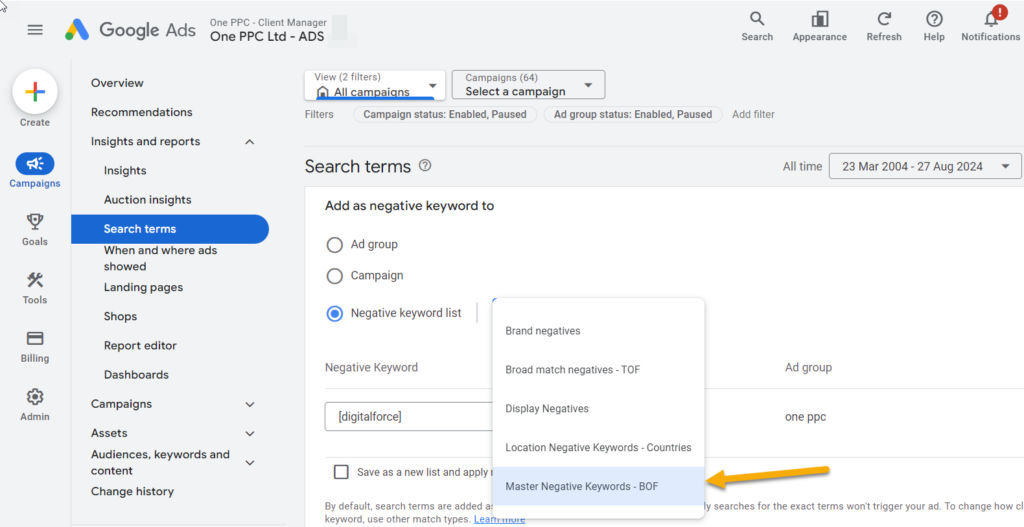
Negative keywords Shopping campaigns are always one of the most easily overlooked parts when building the Shopping structure, yet they strongly affect how the budget flow is distributed across each query. When you correctly understand how a negative keywords Shopping campaigns operates, you will realize it not only helps eliminate irrelevant searches but also creates a clean space for product groups to run at their full potential. This entire process is like fine-tuning a filter for the traffic source—the clearer it is, the more the efficiency increases. And this is precisely what makes Shopping ads smoother, less likely to waste money in the wrong places, and easier to control when scaling.
The Impact of Negative Keywords Shopping Campaigns
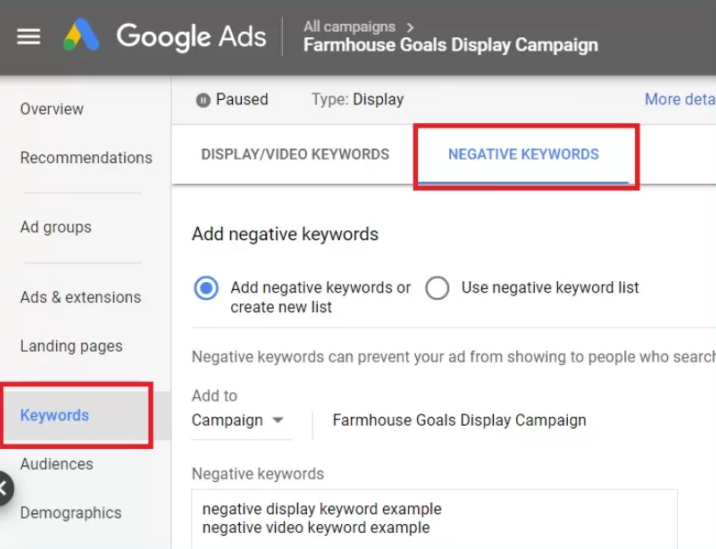
When implementing Google Shopping, everything revolves around query quality. If the stream of searches flowing in is too broad, your data will be skewed, you will waste budget, and you will lose the ability to control the funnel in the right direction. Therefore, focusing on how a negative keywords Shopping campaigns operates will help you tighten the accuracy of traffic, keep your budget cleaner, and create a stable foundation for revenue-driven campaigns.
Negative Keywords Shopping Campaigns
A negative keywords Shopping campaigns is the process of adding negative keywords to prevent your ads from showing up for irrelevant queries. Although Google Shopping does not use keywords for targeting like Search, you still need the negative layer to keep the system from pushing your ads into wrong-context searches. This method helps eliminate noisy traffic, save costs, and increase the clarity of your data. When the negative list is consistently maintained, the ads run for the right products, the right behavior, and at the desired bid price. You can add negative keywords manually or enable the automatic feature for Google to rely on sample lists and filter out inappropriate query groups.
Benefits of Using Negative Keywords
Negative keywords help retain truly valuable queries for Shopping. When off-topic searches are removed, the budget is focused on the exact searches most likely to lead to conversion. This improves the quality of the traffic flow and helps the campaign maintain stability over time. For accounts with many product groups, this negative layer acts as a barrier to prevent items from competing for display against each other.
- Reduce irrelevant traffic: Inappropriate queries are eliminated early to avoid displaying products in the wrong context.
- Improve ROI: You don’t pay for clicks that have no chance of converting, making the return on investment clearer.
- Increase ad relevance: The distribution system focuses more on users with real needs, creating a stream of high-quality potential customers.
Maintaining the negative list not only provides cost benefits but also makes the Shopping structure easier to manage when scaling. With traffic regularly cleaned, the entire campaign has a foundation to achieve stable and more sustainable performance over time.
How to Add Negative Keywords to Shopping Campaigns
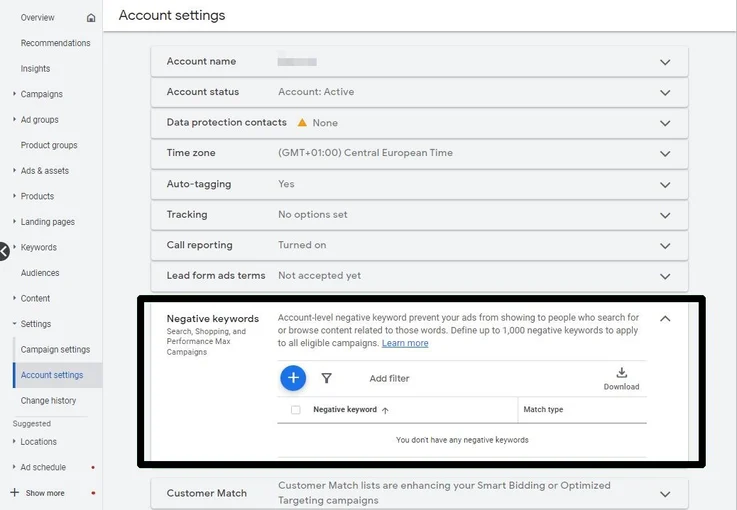
To tightly manage queries and keep the Shopping distribution flow on track, adding negative keywords is a point that needs to be addressed early. The section below follows a clear practical guide, leading you through specific steps to ensure the campaign responds accurately to the buyer’s search intent.
Steps to Add Negative Keywords
Step 1: Log in to your Google Ads account with appropriate access rights.
Step 2: Select the correct Shopping campaign that needs its query scope refined.
Step 3: Navigate to the Keywords section and open Negative Keywords to check the current status.
Step 4: Click the plus icon to start adding a new list.
Step 5: Select the scope of application, either at the campaign level or the ad group level, depending on how you segment your products.
Step 6: Enter the list of negative keywords. Each line corresponds to one keyword for the system to identify more precisely. You can apply different match types.
Example: If you are selling soccer shoes, you might eliminate words like used shoes, sports shoes, or shoe repair to avoid reaching a user group with no intent to buy new products.
Step 7: Click Save to complete the operation and update the query filtering structure.
Methods for Adding Negative Keywords
Once familiar with the operation, you will have two ways to expand or refine the negative list. The first is manual, directly adding phrases that are not relevant to the product, often based on experience and actual query reports. This method is suitable when you need tight control or are looking to reshape the traffic pool.
The second way relies on an automated system. Google Ads has the ability to suggest or actively add negative phrases based on search behavior. This helps quickly filter out low-quality impressions, especially useful when the campaign is running at a large scale. However, you should still check periodically to ensure the negative list does not interfere with reaching valuable queries.
Limitations You Might Encounter When Implementing Negative Keywords
When implementing negative keywords Shopping campaigns, the important thing is not only to eliminate bad queries but also to maintain a sufficiently broad reach so that the product still has room to run. Balancing query blocking and maintaining display capability is often much harder than imagined because the system relies not only on keywords but also reads behavior and context.
Reduced Reach Due to Query Recognition Errors
This phenomenon occurs when the system interprets the query differently from the initial intent. The advertiser might negate a phrase that seems harmless but unintentionally blocks a group of searches with conversion potential. System signals are often built based on commonalities across many queries, so just one incorrect negative point is enough to sweep similar queries along with it. This reduces reach and leads to a sharp decline in traffic without a prior warning sign.
How the System Handles Variant Queries
Variant queries are always the most unpredictable part because users constantly change how they describe products. The system often groups variants into common intent clusters and cross-references them with the negative list. If the negative scope is too broad, the system will eliminate queries that have conversion potential but use different phrasing. In this case, the data will be distorted, and bids will not receive enough necessary signals. This causes a performance drop because the campaign loses quality impressions simply due to an error in intent recognition.
The Role of Historical Data in Determining a Reasonable Negative Scope
Historical data is the foundation for measuring the impact of each query on actual performance. By analyzing queries in detail over time, you can clearly see which groups truly cause waste and which are only temporarily ineffective. Relying on history helps define a reasonable negative boundary without sacrificing growth potential. At the same time, past data also allows the implementer to assess the system’s response rhythm after each change, thereby making negative decisions more accurately and with less risk.
Contact Info
We provide services google ads account for rent nationwide, and with a team of experienced and qualified staff who both support advertising and can directly perform Facebook advertising if you need. Contact us via phone number.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. When the history is noisy due to a data-scarce period, changes in account structure, or seasonal impacts, relying too much on the past will lead to skewed query assessments.
The most effective way is to negate based on distinct behavioral query clusters, monitor the system’s reaction for 48 to 72 hours, and only expand the negative scope when the full cycle of fluctuations has been analyzed. This preserves quality without throttling reach.